


145,93 zł Netto
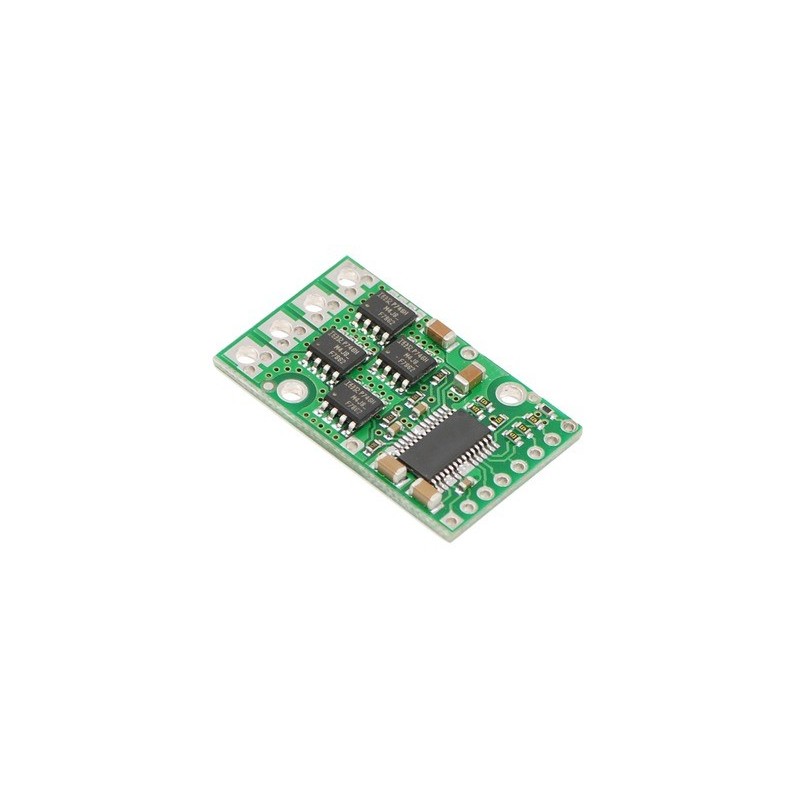
Wysokoprądowy sterownik silnika DC 24v12 umożliwia sterowanie silnikiem DC w systemach do 40 V przy zachowaniu kompaktowych wymiarów i prostego interfejsu PWM/DIR. Moduł sprawdza się w napędach robotów i urządzeń mobilnych wymagających prądu do 12 A bez radiatora, przy możliwości zwiększenia wydajności prądowej przez dodatkowe chłodzenie i odpowiednie filtrowanie zasilania. Pololu 757
Pololu High-Power Motor Driver 24v12 przeznaczony do dwukierunkowego sterowania jednym szczotkowym silnikiem prądu stałego o podwyższonej mocy. Moduł wykorzystuje dyskretny mostek H oparty na tranzystorach MOSFET typu N i obsługuje napięcie zasilania w zakresie 5,5–40 V. Kompaktowa płytka o wymiarach 1,3 × 0,8 cala umożliwia dostarczanie do 12 A prądu ciągłego bez radiatora, a przy dodatkowym chłodzeniu do około 17 A.
Sterownik oferuje prosty interfejs sterowania wymagający dwóch linii sygnałowych, co ułatwia integrację z mikrokontrolerami i sterownikami nadrzędnymi. Obsługa trybów sign-magnitude oraz locked-antiphase umożliwia dobór sposobu regulacji prędkości i kierunku do wymagań aplikacji. Zintegrowana detekcja wybranych zwarć oraz sygnalizacja stanów awaryjnych na wyjściach FF1 i FF2 zwiększają odporność na typowe błędy okablowania.
Układ nie posiada sprzętowej ochrony przed odwrotną polaryzacją ani zabezpieczeń nadprądowych i temperaturowych, dlatego w aplikacjach pracujących blisko granic parametrów zalecane jest stosowanie odpowiednio dobranej pojemności filtrującej przy zasilaniu, zapewnienie chłodzenia oraz monitorowanie prądu z wykorzystaniem zewnętrznego czujnika.
Cechy
Producent BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Osoba odpowiedzialna BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Pololu G2 24v13 High Power to miniaturowy sterownik silnika DC. Zasilanie sterownika: 6,5 - 40 V. Wydajność prądowa modułu: 13 A. Moduł posiada zabezpieczenie przed napięciem wstecznym i przepięciami. Pololu 2992
Brak towaru
Pololu G2 18v17 to miniaturowy sterownik silnika DC. Zasilanie sterownika: 6,5 - 30 V. Wydajność prądowa modułu: 17 A.
Moduł posiada zabezpieczenie przed napięciem wstecznym i przepięciami. Pololu 2991
Brak towaru
Moduł pozwala połączyć zalety Raspberry Pi i Arduino, wyposażony jest w mikrokontroler ATmega32u4 z botloaderem zgodnym z Arduino i podwójny sterownik silników. Pololu 3119
Moduł pozwala połączyć zalety Raspberry Pi i Arduino, wyposażony jest w mikrokontroler ATmega32u4 z botloaderem zgodnym z Arduino i podwójny sterownik silników. Pololu 3118
Moduł rozszerzeń (shield) ze sterownikiem silnika krokowego dla Arduino. Pozwala na sterowanie napędami pracującymi z napięciem do 40 V i poborem prądu do 2 A na cewkę. DFRobot DRI0035
Brak towaru
DRV8825 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier to sterownik silnika krokowego z układem DRV8825, pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 1,5A na fazę, bez użycia radiatora. Układ może być zasilany napięciem do 45V, w zestawie znajduje się radiator. Jest kompatybilny z Pololu 2133
Brak towaru
Sterownik silnika krokowego z układem Allegro A4988 (A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier) pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 2A na fazę. Układ może być zasilany napięciem do 35V, w zestawie znajduje się radiator. Jest kompatybilny z Pololu 1182
Sterownik silnika krokowego, napięcie zasilania cewek silnika 6..30 V, napięcie pracy logiki sterownika 0..5 V lub 0..3,3 V. Możliwa regulacja prądu sterowania na fazę obrotu podczas pracy sterownika. ROB-12779
Brak towaru
Pololu G2 18v25 to miniaturowy sterownik silnika DC. Zasilanie sterownika: 6.5V...30V. Wydajność prądowa modułu: 25A.
Moduł posiada zabezpieczenie przed napięciem wstecznym i przepięciami. Pololu 2994
Brak towaru
Pololu G2 24v21 to miniaturowy sterownik silnika DC. Zasilanie sterownika: 6.5V...40V. Wydajność prądowa modułu: 21A.
Moduł posiada zabezpieczenie przed napięciem wstecznym i przepięciami. Pololu 2995
Sterownik silnika krokowego A4988 operujący na napięciach 8..35 V i prądzie 1,2 A. Pololu 2128
Rozszerzenie dla Raspberry Pi z dwoma sterownikami silników obsługującymi zakres napięć 5-28 V i prąd ciągły 3 A (chwilowy 5 A) każdy. Pololu 2755
Brak towaru
Sterownik silnika krokowego AMIS-30543 operujący w zakresie napięć 6..30 V i prądzie 1,8 A. Pololu 2970
Niewielka płytka z sterownikiem silnika szczotkowego MAX14870 działającym w napięciach od 4,5V do 36V i prądzie ciągłym 1,7 A (2,5 A chwilowym). Pololu 2961
Dwukanałowy sterownik silników DC oparty na ukłądzie HR9933. Pozwala na kontrolowanie ruchu napędów o napięciu zasilania do 10 V i poborzę prądu do 1,5 A. DFRobot DRI0040
Jednokanałowy sterownik silnika DC, który może kontrolować ruch napędu o napięciu zasilania do 36 V i poborze prądu do 15 A. Sterowany za pomocą sygnału PWM. DFRobot DRI0042

Wysokoprądowy sterownik silnika DC 24v12 umożliwia sterowanie silnikiem DC w systemach do 40 V przy zachowaniu kompaktowych wymiarów i prostego interfejsu PWM/DIR. Moduł sprawdza się w napędach robotów i urządzeń mobilnych wymagających prądu do 12 A bez radiatora, przy możliwości zwiększenia wydajności prądowej przez dodatkowe chłodzenie i odpowiednie filtrowanie zasilania. Pololu 757
