


49,30 zł Netto
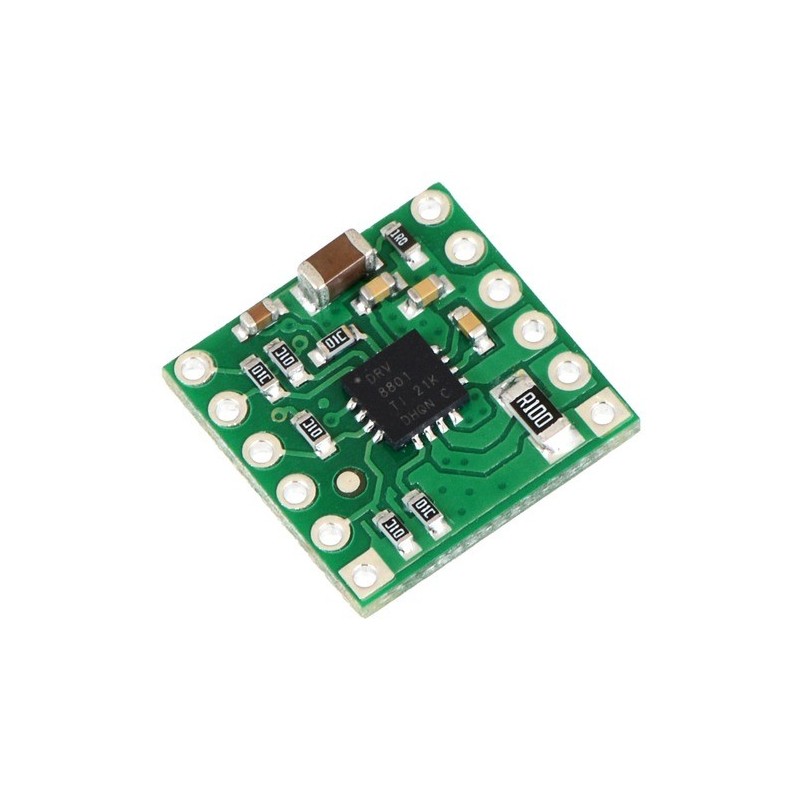
Wydajny, kompaktowy i prosty w użyciu sterownik silnika DC, idealny do projektów robotycznych, automatyki oraz prototypów edukacyjnych. Dzięki szerokiemu zakresowi napięć, niewielkiej liczbie wymaganych linii sterujących i wbudowanym zabezpieczeniom doskonale sprawdzi się zarówno u początkujących, jak i zaawansowanych konstruktorów szukających nowoczesnej alternatywy dla starszych mostków H. Pololu 2136
Kompaktowa płytka sterownika silnika DC oparta na układzie DRV8801 firmy Texas Instruments. Umożliwia dwukierunkowe sterowanie jednym szczotkowym silnikiem prądu stałego przy napięciu zasilania silnika od 8 do 36 V. Jest to nowoczesna i wydajna alternatywa dla klasycznych sterowników takich jak L293D czy L298N, oferująca wyższą sprawność, mniejsze straty mocy oraz wbudowane zabezpieczenia.
Sterowanie odbywa się za pomocą prostego interfejsu: jednego pinu do wyboru kierunku obrotów oraz jednego pinu PWM do regulacji prędkości.
Cechy
Producent BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Osoba odpowiedzialna BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Moduł sterownika silnika krokowego DRV8825 dla Arduino. Pozwala na sterowanie dwoma napędami, wyposażony w złącze XBee. DFRobot DRI0023
Sterownik silnika krokowego z układem MP6500 pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 1,5A na fazę, bez użycia radiatora. Układ może być zasilany napięciem w zakresie 4,5-35V. Pololu 2966
Sterownik silnika krokowego z układem MP6500 pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 1,8A na fazę, bez użycia radiatora. Układ może być zasilany napięciem w zakresie 4,5...35 V. Pololu 2968
Gravity: IO Expansion & Motor Driver Shield to płytka rozszerzeń kompatybilna z Arduino, która udostępnia cyfrowe porty I/O, piny analogowe interfejsy I2C, SPI i UART, a także sterownik silników DC. DFRobot DFR0502
Tic T500 USB Multi-Interface Stepper Motor Controller to sterownik silnika krokowego oparty na układzie MP6500. Pozwala on sterować silnikiem krokowym, którego napięcie na cewkę wynosi 4,5...35V, maksymalny prąd na cewkę wynosi do 1,5A. Sterownikiem można sterować przy pomocy: USB, TTL, I2C, RC (PWM modelarski), wejściem analogowym czy enkodera kwadraturowego. Pololu 3135
Tic T500 USB to sterownik silnika krokowego oparty na układzie MP6500. Pozwala on sterować silnikiem krokowym, którego napięcie na cewkę wynosi 4,5-35V, maksymalny prąd na cewkę wynosi do 1,5A. Sterownikiem można sterować przy pomocy: USB, TTL, I2C, RC (PWM modelarski) itp. Pololu 3134
Sterownik silnika prądu stałego (DC) o napięciu pracy 6-34V i maksymalnym prądzie ciągłym 30A. Posiada możliwość łatwej realizacji pętli sprzężenia zwrotnego oraz liczne systemy bezpieczeństwa. Pololu 3290
Sterownik silnika prądu stałego (DC) o napięciu pracy 6...34V i maksymalnym prądzie ciągłym 60A. Posiada możliwość łatwej realizacji pętli sprzężenia zwrotnego oraz liczne systemy bezpieczeństwa. Pololu 3291
Brak towaru
2x1.2A DC Motor Driver to podwójny sterownik silników DC ze złączem Gravity, zasilanych napięciem 2,5...12V o maksymalnym poborze prądu 1,2A (3,2A w szczycie) na kanał. DFRobot DRI0044-A
2x1.2A DC Motor Driver to podwójny sterownik silników DC zasilanych napięciem 2,5-12V o maksymalnym poborze prądu 1,2A (3,2A w szczycie) na kanał. DFRobot DRI0044
Nakładka do STM32 Nucleo ze sterownikiem niskonapięciowego, trójfazowego silnika BLDC. Shield oparty jest na układzie STSPIN233. Świetnie nadaje się do sterowania silnikami w aplikacjach mobilnych, takich jak roboty, zabawki oraz drukarki termiczne. Nakładka wyposażona jest w złącze zgodne ze standardem Arduino UNO R3. X-NUCLEO-IHM17M1
Brak towaru
Dual MAX14870 Motor Driver to podwójny sterownik silników DC kompatybilny ze standardem Arduino pozwalający na wysterowanie dwóch silników DC napięciem 4,5-36V prądem ciągłym 1,7A. Pololu 2519
Dual MAX14870 Motor Driver to podwójny sterownik silników DC kompatybilny z Raspberry Pi pozwalający na wysterowanie dwóch silników DC napięciem 4,5-36V prądem ciągłym 1,7A. Pololu 3759
Dual MAX14870 Motor Driver to podwójny sterownik silników DC kompatybilny ze standardem Raspberry Pi pozwalający na wysterowanie dwóch silników DC napięciem 4,5-36V prądem ciągłym 1,7A. Pololu 3758
Sterownik silnika prądu stałego (DC) o napięciu pracy 6,5-30V i maksymalnym prądzie ciągłym 19A. Posiada możliwość łatwej realizacji pętli sprzężenia zwrotnego oraz liczne interfejsy sterujące. Pololu 3146
Sterownik silnika prądu stałego (DC) o napięciu pracy 6,5-40V i maksymalnym prądzie ciągłym 13A. Posiada możliwość łatwej realizacji pętli sprzężenia zwrotnego oraz liczne interfejsy sterujące. Pololu 3147

Wydajny, kompaktowy i prosty w użyciu sterownik silnika DC, idealny do projektów robotycznych, automatyki oraz prototypów edukacyjnych. Dzięki szerokiemu zakresowi napięć, niewielkiej liczbie wymaganych linii sterujących i wbudowanym zabezpieczeniom doskonale sprawdzi się zarówno u początkujących, jak i zaawansowanych konstruktorów szukających nowoczesnej alternatywy dla starszych mostków H. Pololu 2136
