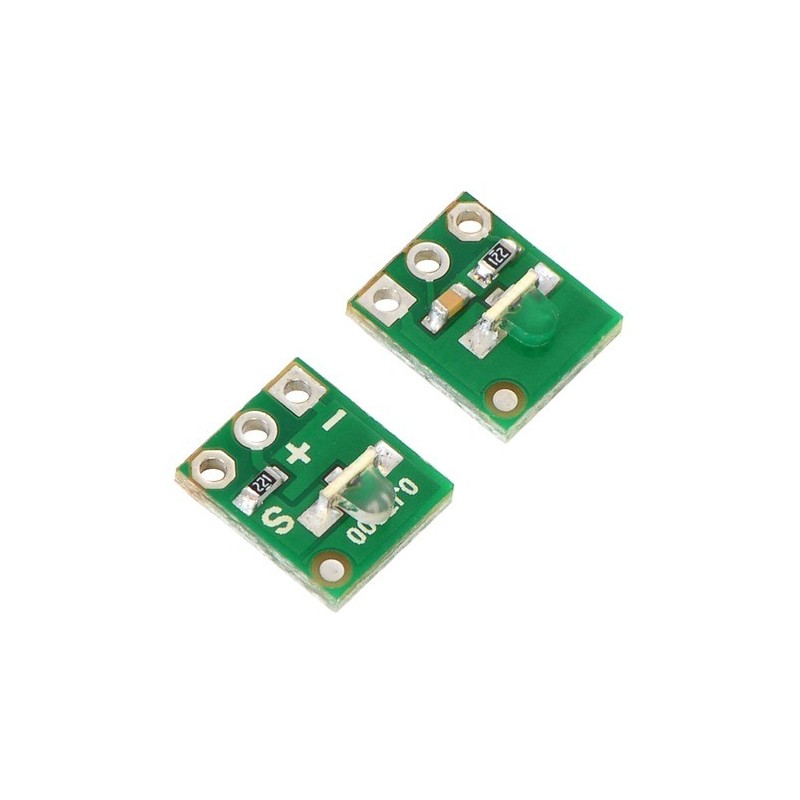

The QTR-L-1RC reflectance sensor incorporates a right-angle infrared LED and a right-angle phototransistor in an inexpensive, tiny 0.35" A— 0.3" module that can be mounted almost anywhere and is great for edge detection and line following. The output is designed to be measured by a digital I/O line. This sensor is sold in packs of two units.
Note: The QTR-L-1RC reflectance sensor requires a digital I/O line to take readings. The similar QTR-L-1A reflectance sensor is available with an analog output.
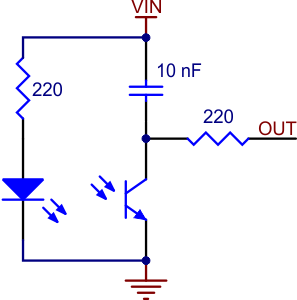 |
The Pololu QTR-L-1RC reflectance sensor carries a right-angle infrared LED and a right-angle phototransistor, both pointing toward the front edge of the board. The phototransistor uses a capacitor discharge circuit that allows a digital I/O line on a microcontroller to take an analog reading of reflected IR by measuring the discharge time of the capacitor. Shorter capacitor discharge time is an indication of greater reflection.
The LED current-limiting resistor is set to deliver approximately 17 mA to the LED when VIN is 5 V. The current requirement can be met by some microcontroller I/O lines, allowing the sensor to be powered up and down through an I/O line to conserve power.
This sensor was designed to be used with the board perpendicular to the surface being sensed, and narrow-angle lenses built into the infrared LED and phototransistor packages allow it to be effective to a range of about 1" (25 mm). Because of its small size, multiple units can easily be arranged to fit various applications such as line sensing and proximity/edge detection. The QTR-L-1RC is sold in packs of two units.
For a similar sensor that can be used with the board parallel to the surface, but with shorter range, please see the QTR-1RC reflectance sensor. We also offer arrays of three and eight sensors: the QTR-3RC reflectance sensor array and the QTR-8RC reflectance sensor array.
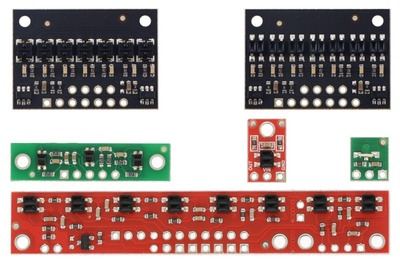 |
| QTR sensor size comparison. Clockwise from top left: QTR-3RC, QTR-1RC, QTR-L-1RC, QTR-8RC. |
|---|
 |
Like the Parallax QTI, the QTR-L-1RC module has sensor outputs that require a digital I/O line capable of first charging the output capacitor (by driving the line high) and then measuring the time for the capacitor to discharge through the phototransistor. This measurement approach has several advantages, especially when multiple units are used:
The typical sequence for reading a sensor is:
These steps can typically be executed in parallel on multiple I/O lines.
With a strong reflectance, the discharge time can be as low as several dozen microseconds; with no reflectance, the discharge time can be up to a few milliseconds. The exact time of the discharge depends on your microcontroller’s I/O line characteristics. Meaningful results can be available within 1 ms in typical cases (i.e. when not trying to measure subtle differences in low-reflectance scenarios), allowing up to 1 kHz sampling. The following table shows some typical discharge times (from 5 V down to a 2 V threshold) of the sensor over different surfaces and at different distances:
| White surface | 3/4" black electrical tape | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.25" distance | 100 ÎLs | 320 ÎLs |
| 1" distance | 160 ÎLs | 260 ÎLs |
Ambient light, especially sunlight, can affect the sensor readings significantly. If the discharge time of the QTR-L-1RC is consistently low, you might need to add shielding around the sensor or mount it in a different location to reduce interference from outside light sources.
Our Pololu AVR library provides functions that make it easy to use these sensors with our Orangutan robot controllers; please see the QTR Reflectance Sensors section of our library command reference for more information. We also have a Arduino library for these sensors.
Each pack of two reflectance sensors includes sets of straight male header strips and right-angle male header strips, which allow you to mount them in the orientation of your choice. You can also solder wires, such as ribbon cable, directly to the pads for the most compact installation.
|
|
 |
QTR-L-1A Reflectance Sensor (2-Pack) |
 |
QTR-1RC Reflectance Sensor |
 |
Female Crimp Pins for 0.1" Housings 100-Pack |
Producent BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Osoba odpowiedzialna BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Moduł pozwala na pomiar oświetlenia w otoczeniu czujnika. Zakres pomiarowy mieści się w przedziale od 1 do 65535 LUX, a komunikacja odbywa się przy użyciu magistrali I2C. DFRobot SEN0097
Moduł z 11-kanałowym czujnikiem AS7341 pozwalający na wykrywanie światła w różnych zakresach długości fali (detekcja kolorów). Komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. Waveshare AS7341 Spectral Color Sensor
Moduł z czujnikiem koloru i natężenia światła. Oferuje szeroki zakres wykrywania i dwie diody podświetlające LED. Komunikuje się poprzez magistralę I2C. Pimoroni PIM375
Moduł z czujnikiem światła oraz czujnikiem zbliżeniowym do 5 cm. Pozwala odczytać natężenie oświetlenia od 0,01 do 64000 lux i komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. Pimoroni PIM413
Moduł z czujnikiem światła UV LTR390-UV. Pozwala na pomiar natężenia promieniowania ultrafioletowego i światła widzialnego. Komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. Waveshare UV Sensor (C)
Moduł z czujnikiem natężenia światła TSL2591. Wyposażony w złacze STEMMA QT z interfejsem I2C. Adafruit 1980
Moduł z czujnikiem natężenia światła BH1750. Zakres pomiarowy mieści się w przedziale od 1 do 65535 lux, a komunikacja odbywa się przy użyciu magistrali I2C. Adafruit 4681
Moduł ze czujnikiem zbliżeniowym i światła otoczenia oparty na układzie VCNL4040. Pozwala na wykrywanie przeszkód w zakresie od 0 do 20 cm. Komunikuje się poprzez magistralę I2C. Adafruit 4161
Moduł z 10-kanałowym czujnikiem AS7341 pozwalający na wykrywanie światła w różnych zakresach długości fali (detekcja kolorów). Komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. Adafruit 4698
Moduł z czujnikiem światła UV LTR390-UV. Pozwala na pomiar natężenia promieniowania ultrafioletowego i światła widzialnego. Wyposażony w złącze STEMMA QT, komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. Adafruit 4831
Moduł z czujnikiem światła w postaci fotorezystora. Na płytce umieszczono komparator i potencjometr. Moduł ma wyjście cyfrowe
Brak towaru
Moduł z analogowym czujnikiem TEMT6000. Napięcie na wyjściu zwiększa się wraz ze wzrostem natężenia padającego światła. Czujnik zasilany jest napięciem 5 V
Moduł z cyfrowym czujnikiem natężenia światła MAX44009. Zasilany jest napięciem od 1,7 do 3,6 V i komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. GY-49
Moduł z analogowym czujnikiem światła UV ML8511. Umożliwia pomiar natężenia promieniowania dla fali UV-A (320-400nm) i UV-B (280-320nm). Ma interfejs analogowy. GY8511
Moduł z czujnikiem koloru TCS3472. Płytka została wyposażona w złącze Grove i komunikuje się przez interfejs I2C. M5Stack U009
Czujnik koloru o zasiegu od 8 do 16 mm. Oferuje 3 tryby pracy i może być zasilany napięciem od 12 do 24 V. DFRobot SEN0506

