- Obecnie brak na stanie
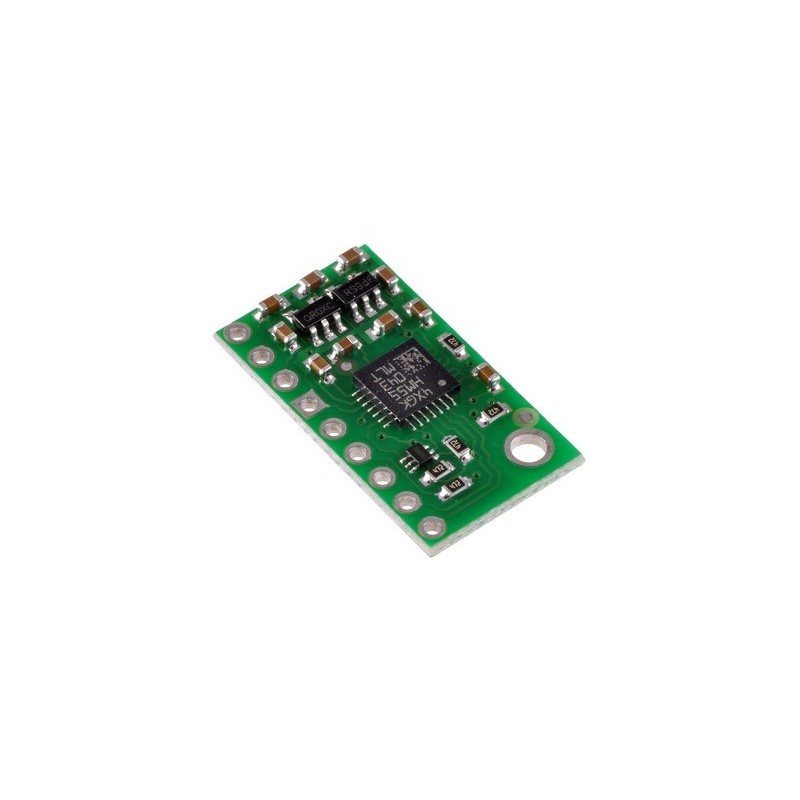

LSM303DLM Kompas 3D i akcelerometr ze stabilizatorami napięcia
LSM303DLM łączy w sobie funkcjonalność cyfrowego, 3-osiowego akcelerometru oraz 3-osiowego magnetometru, które to połączenie jest wręcz stworzone do budowy kompasu z kompensacją odchylenia. Sześć niezależnych odczytów, których czułość może być ustawiona w zakresach ±2 do ±8 g i ±1.3 do ±8.1 gauss, jest dostępnych przez interfejs I2C. Płytka zawiera stabilizatory napięcia i pozwala na operowanie napięciem rzędu 2,6 do 5,5 V, a standardowe wyprowadzenia w rastrze 2,54mm (pasuje do tzw. goldpinów) ułatwia wykorzystanie jej ze standardowymi płytkami uniwersalnymi i prototypowymi.
 |
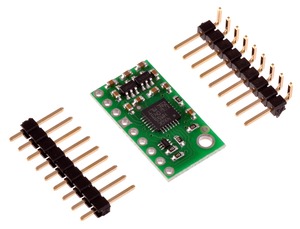
LSM303DLM to dobry układ, ale jego małe wymiary sprawiają, że jego wykorzystanie może sprawić hobbyście kłopoty. Urządzenie wymaga także dwóch różnych napięć zasilania, które zwykle nie występują w jednym układzie. Sprzedawana przez nas płytka rozwiązuje te problemy, przez zastosowanie dodatkowych elementów, takich jak 2 stabilizatory napięcia i obwód zmiany poziomów napięć, jednocześnie zachowując minimalne wymiary. Płytka jest przez nas dostarczana w pełni polutowana, od razu gotowa do użycia - jak na zdjęciu.
LSM303 posiada wiele konfigurowalnych opcji, wliczając w to dynamicznie wybierane zakresy/czułości dla akcelerometra i magnetometru, szybkość transferu danych i dwa niezależnie-programowalne zewnętrzne przerwania (wykorzystujące dwa piny).Magnetometr oraz akcelerometr, mogą być niezależnie włączane lub wyłączane, aby oszczędzać energię, a specjalne funkcja pozwala wybudzić i uśpić akcelerometr za pomocą zewnętrznego przerwania. 6 niezależnych odczytów z magnetometru i akcelerometru (czasami nazywane 6DoF) jest dostępnych przez magistralę I2C/TWI. Interfejs ten może być z powodzeniem wykorzystany w wielu aplikacjach, wliczając w to kompas z kompensacją odchylenia, który może zostać wykorzystany do określenia kierunków niezależnie od ustawienia płytki.
Płytka zawiera dwa stabilizatory, które dostarczają napięcia 1,8V i 3V, niezbędne do prawidłowej pracy układu LSM303. Umożliwia to zasilenie z tylko jednego źródła napięcia 2,6 ÷ 5,5V. Napięcia ze stabilizatorów są różwnież wyprowadzone na piny płytki i mogą dostarczyć dodatkowym peryferiom aż do 150mA dla 1,8V i 300mA dla 3V. Płytka zwiera również specjalny obwód, który umożliwia dopasowanie napięć linii danych do poziomu napięcia dostarczanego do VIN, co znacznie ułatwia integrację modułu z systemami zasilanymi z 3,3V lub 5V.
 |
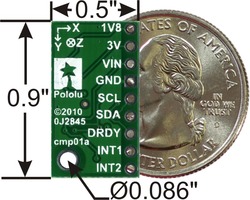
Przynajmniej 4 połączenia są wymagane do obsługi LSM303DLM: VIN, GND, SCL i SDA. VIN powinno być połączone do 2,6 ÷ 5,5 V, GND do 0 V, a SCL i SDA do magistrali I2C dopasowanej poziomami logicznymi do VIN.
|
|
| PIN | Opis |
|---|---|
| VIN | To jest główny pin zasilania modułu. Wymagane napięcie to 2,6 ÷ 5,5 V. Napięcia poziomów linii SCL i SDA są dopasowywane do tego napięcia. |
| GND | Masa (0 V) wymagana przy podłączaniu zasilania. Masa powinna być wspólna dla modułu, jak i dla układu, który będzie tym modułem stertować. |
| 1V8 | Wyjście stabilizatora 1,8V. Umożliwia dodatkowym peryferiom pobór prądu aż do 150mA. |
| 3V | Wyjście stabilizatora 3V. Umożliwia dodatkowym peryferiom pobór prądu aż do 300mA. |
| SCL | Linia I2C: stan wysoki jest równy VIN, a niski 0 V |
| SDA | Linia I2C: stan wysoki jest równy VIN, a niski 0 V |
| DRDY | Wskaźnik gotowości danych do odczytu, dla magnetometru. Poziom logiczny 1,8V. Stan wysoki oznacza, że dane z magnetometru są gotowe do odczytu. |
| INT1 | Przerwanie 1 - 1,8V-stan-logiczny |
| INT2 | Przerwanie 2 - 1,8V-stan-logiczny |
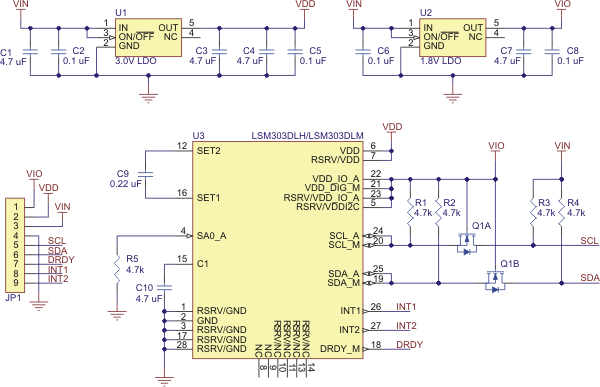 |
The above schematic shows the additional components the carrier board incorporates to make the LSM303 easier to use, including the voltage regulators that allow the board to be powered from a single 2.6 – 5.5 V supply and the level-shifter circuit that allows for I˛C communication at the same logic voltage level as VIN.
The LSM303DLM readings can be queried and the device can be configured through the I˛C bus. The module acts as two chained I˛C slave devices, with the accelerometer and magnetometer clock and data lines tied together to the same I˛C bus to ease communication. Additionally, level shifters on the I˛C clock (SCL) and data lines (SDA) enable I˛C communication with microcontrollers operating at the same voltage as VIN (2.6 – 5.5V). A detailed explanation of the protocol can be found in the LSM303DLM datasheet (519k pdf), and more detailed information about I˛C in general can be found in NXP’s I˛C-bus specification (371k pdf).
The accelerometer and the magnetometer have separate 7-bit slave addresses on the I˛C bus. The magnetometer’s slave address is 0011110b and cannot be changed. The accelerometer’s slave address has its least significant bit (LSb) determined by the voltage on the slave address selector pad (SA0_A). The carrier board pulls SA0_A to ground through a 4.7kΩ resistor, setting the accelerometer’s slave address to 0011000b by default. If the accelerometer’s selected slave address happens to conflict with some other device on your I˛C bus, it is possible to access SA0_A through the untented via on the bottom of the board and pull it up.
In our tests of the board, we were able to communicate with the chip at clock frequencies up to 400 kHz; higher frequencies might work but were not tested. The chip itself and carrier board do not meet of some requirements to make the device compliant with I˛C fast-mode. It is missing 50ns spike suppression on the clock and data lines, and additional pull-ups on the clock and data lines might also be necessary to achieve compliant signal timing characteristics.
The datasheet provides all the information you need to use this sensor, but picking out the important details can take some time. Here are some pointers for communicating with and configuring the LSM303DLM that we hope will get you up and running a little bit faster:
The inertial interrupts (INT1 and INT2) are highly configurable 1.8V-level outputs that can change due to accelerations (the magnetometer has no effect on INT1 or INT2). If the sleep-to-wakeup feature of the accelerometer is enabled, when an interrupt is triggered, the accelerometer wakes up.
 |
MinIMU-9 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass (L3G4200D and LSM303DLM Carrier) |
 |
66-Channel LS20031 GPS Receiver Module |
 |
0.100" (2.54 mm) Breakaway Male Header: 1x40-Pin, Straight |
Producent BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Osoba odpowiedzialna BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
HK 10x4.7 SF Carbon Fiber Propellers L/H and R/H Rotation (1 pair) (39773)
Brak towaru
Brak towaru
HK Hobbyking YEP 90A (2-6S) Brushless Speed Controller with Selectable SBEC (40275)
Brak towaru
HK Turnigy nano-tech 6000mah 2S2P 65~130C Hardcase Lipo Pack (17265)
Brak towaru
HK NTM Prop Drive Series 28-26A 1200kv / 286w (17345)
Brak towaru
HK RGB LED Flexible Strip with 4-pin Driver Connector 500mm (Red/Green/Blue) (17406)
Brak towaru
HK RGB LED Flexible Strip with 4-pin Driver Connector 1m (Red/Green/Blue) (17407)
Brak towaru
HK Clear Foam Glue (Medium Cure) - Large 100ml (17535)
Brak towaru
Helikopter mikro zdalnie sterowany, współosiowy, 2.4Ghz, 4-kanałowy, nadajnik Dual-mode, RTF (HK17580)
Brak towaru
HK HobbyKing 1500mAH LiFe 3S 9.9v Transmitter pack. (17955)
Brak towaru
Brak towaru
Xilinx Kintex®-7 XC7K325T-1FFG676 FPGA - zestaw uruchomieniowy
Brak towaru
COM-12656 - EasyVR Shield 2.0 - Voice Recognition Shield, RoHS
Brak towaru
Brak towaru
Brak towaru
Arduino Intel Galileo to platforma z SoC Intel Quark X1000 kompatybilna z Arduino, złącza są analogiczne z Arduino Uno R3. Możliwe jest stosowanie shieldów 3,3 V oraz 5 V. Na pokładzie są m.in. złącze mini-PCI Express, Ethernet 100 Mb, gniazdo kart micro-SD, pamięć Flash. E000037
Brak towaru

LSM303DLM Kompas 3D i akcelerometr ze stabilizatorami napięcia
