


36,56 zł Netto
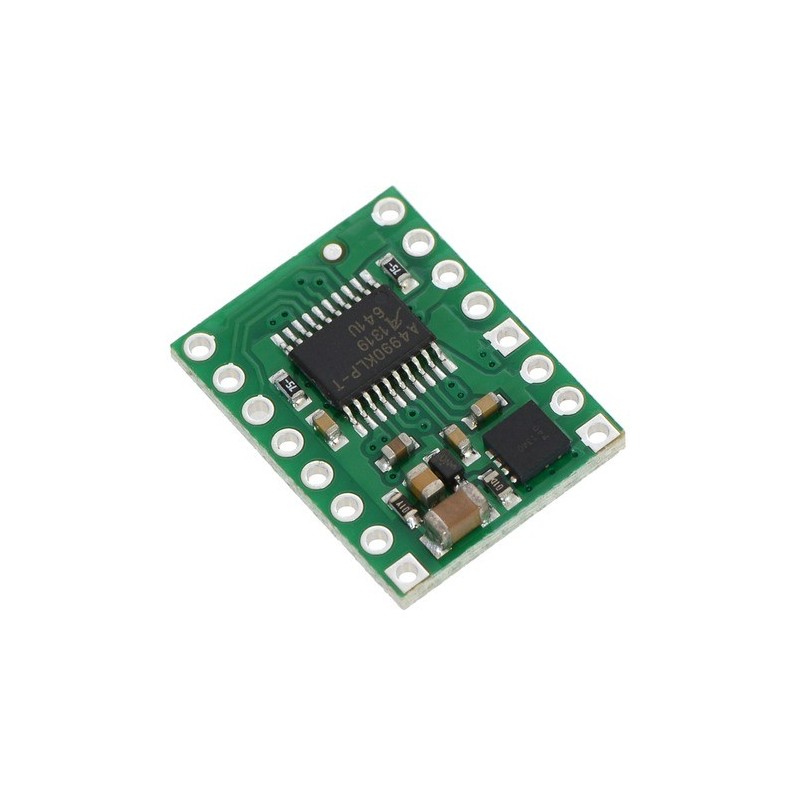
Sterownik silników A4990 stanowi solidne i bezpieczne rozwiązanie do sterowania dwoma silnikami DC przy napięciach do 32 V. Dzięki wbudowanemu ograniczeniu prądu, licznym zabezpieczeniom oraz kompaktowej formie moduł sprawdzi się w projektach wymagających niezawodnej pracy, ochrony elektroniki oraz prostego sterowania z mikrokontrolera. Pololu 2137
Sterownik A4990 to kompaktowy moduł sterownika silników oparty na układzie A4990 firmy Allegro MicroSystems, przeznaczony do dwukierunkowego sterowania dwoma szczotkowymi silnikami DC lub jednym silnikiem krokowym bipolarnym. Moduł obsługuje szeroki zakres napięć zasilania od 6 do 32 V, dzięki czemu znajduje zastosowanie w projektach robotycznych, automatyce oraz układach mobilnych zasilanych z wyższych napięć.
Płytka zawiera komplet elementów SMD, w tym rezystory pomiarowe prądu oraz dodatkowy tranzystor MOSFET zapewniający ochronę przed odwrotną polaryzacją zasilania.
Cechy
Producent BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Osoba odpowiedzialna BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Polska sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Moduł 3-kanałowego sterownika silników szczotkowych z funkcją miksowania sygnałów PWM. Pozwala sterować trzema silnikami DC o poborze prądu do 3 A na kanał
Moduł sterownika ESC do silnika bezszczotkowego o wydajności prądowej do 40 A. Może współpracować z pakietami LiPo od 3S do 6S. Wykorzystuje oprogramowanie BLHeli_32. Skystars Talon32
Moduł sterownika ESC do silnika bezszczotkowego o wydajności prądowej do 120 A. Może współpracować z pakietami LiPo od 5S do 12S. Wykorzystuje oprogramowanie BLHeli_32. FLYCOLOR X-CROSS HV
Moduł sterownika ESC do silnika bezszczotkowego o wydajności prądowej do 80 A. Może współpracować z pakietami LiPo od 5S do 12S. Wykorzystuje oprogramowanie BLHeli_32. FLYCOLOR X-CROSS HV
Moduł programujący do sterowników ESC z serii AM32 i BLS32. Pozwala w łatwy sposób zaktualizować oprogramowanie sterownika przez złącze USB typu C. RhinoESC Crawler
Panelowy kontroler prędkości silnika szczotkowego UX-52 to wszechstronne urządzenie z regulacją prędkości od 90 do 1400 obr./min. Oferuje precyzyjną kontrolę nad silnikami o napięciu wejściowym 220VAC, charakteryzując się solidną konstrukcją i wygodnym wyświetlaczem cyfrowym.
Miniaturowy sterownik ESC silnika bezszczotkowego 7A 1-2S BLheli_S XSD7A to kompaktowe urządzenie o dużej wydajności, idealne do kontroli silników bezszczotkowych w małych projektach. Dzięki niskiej wadze i solidnej mocy, nadaje się do dronów, modeli RC i innych aplikacji wymagających precyzyjnej kontroli silnika.
Sterownik, który umożliwia kontrolę dowolnego 3-fazowego silnika BLDC. Wyposażony został w wbudowaną łączność WiFi i Bluetooth oraz zintegrowany czujnik efektu Halla TMAG5273 i wzmacniacze czujników prądu INA240A1, dzieki czemu pozwala na wykrozystanie zaawansowanych algorytmów FOC. SparkFun ROB-22132
Moduł ze sterownikiem silnika krokowego oparty na układzie DRV8434. Pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 1,2 A na fazę i napięciem od 4,5 V do 48 V. Pololu 3762
Moduł ze sterownikiem silnika krokowego oparty na układzie DRV8434. Pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 1,2 A na fazę i napięciem od 4,5 V do 48 V. Pololu 3763
Moduł ze sterownikiem silnika krokowego oparty na układzie DRV8834. Pozwala na zasilanie silnika bipolarnego prądem do 2 A na fazę, bez użycia radiatora. Układ może być zasilany napięciem do 10,8 V. Pololu 2134
KAmod Motor Driver to zaawansowany sterownik silnika DC zasilany napięciem 6-30 V, umożliwiający regulację mocy metodą PWM oraz kontrolę kierunku obrotów, kompatybilny z sygnałami analogowymi i PWM z różnych źródeł, wyposażony w zabezpieczenia przeciążeniowe i termiczne oraz funkcje łagodnego startu i zatrzymania
Zaawansowany sterownik silnika krokowego Nema 23 z serii CLRS, zaprojektowany do precyzyjnych zastosowań przemysłowych z komunikacją sieciową RS485 (Modbus RTU). Eliminuje ryzyko utraty kroków dzięki zamkniętej pętli sprzężenia zwrotnego i oferuje wsparcie dla trybów: pozycjonowania (Profile Position), prędkości (Velocity), powrotu do pozycji referencyjnej (Homing) oraz PR Mode z 16-pozycyjną tabelą sterowania punkt-do-punktu. Sterownik obsługuje do 31 osi w jednej sieci, oferuje prąd do 7 A, napięcie zasilania od 20 do 50 VDC i chłodzenie pasywne lub aktywne, co czyni go niezawodnym rozwiązaniem dla robotyki, automatyki i systemów CNC. CL2C-RS57
Kompaktowy sterownik, który umożliwia precyzyjne sterowanie bipolarnymi silnikami krokowymi. Oferuje dużą precyzję ruchu dzięki możliwości sterowania silnikiem krokowym z rozdzielczością do 1/128 kroku oraz dwa interfejsy sterujące - sterowanie krokowe typu clock-in oraz komendy szeregowe. SparkFun ROB-25167
Kompaktowy i wydajny moduł przeznaczony do precyzyjnego sterowania bipolarnymi silnikami krokowymi, oferujący mikrostepping do 1/32 kroku oraz maksymalny prąd do 2 A w trybie szczytowym. Dzięki zaawansowanym funkcjom, takim jak algorytm QuietStep (APFD), wbudowane zabezpieczenia oraz kompatybilność pinowa z A4988, doskonale sprawdzi się w projektach hobbystycznych, edukacyjnych i przemysłowych. Wersja Blue Edition z czterowarstwową płytką i miedzią 2 oz zapewnia lepsze odprowadzanie ciepła, zwiększając niezawodność pracy nawet przy wyższych obciążeniach. Pololu 5340
Kompaktowy i wydajny moduł przeznaczony do precyzyjnego sterowania bipolarnymi silnikami krokowymi, oferujący mikrostepping do 1/32 kroku oraz maksymalny prąd do 2 A w trybie szczytowym. Dzięki zaawansowanym funkcjom, takim jak algorytm QuietStep (APFD), wbudowane zabezpieczenia oraz kompatybilność pinowa z A4988, doskonale sprawdzi się w projektach hobbystycznych, edukacyjnych i przemysłowych. Wersja Blue Edition z czterowarstwową płytką i miedzią 2 oz zapewnia lepsze odprowadzanie ciepła, zwiększając niezawodność pracy nawet przy wyższych obciążeniach. Pololu 5341

Sterownik silników A4990 stanowi solidne i bezpieczne rozwiązanie do sterowania dwoma silnikami DC przy napięciach do 32 V. Dzięki wbudowanemu ograniczeniu prądu, licznym zabezpieczeniom oraz kompaktowej formie moduł sprawdzi się w projektach wymagających niezawodnej pracy, ochrony elektroniki oraz prostego sterowania z mikrokontrolera. Pololu 2137
