









zł161.79 tax excl.
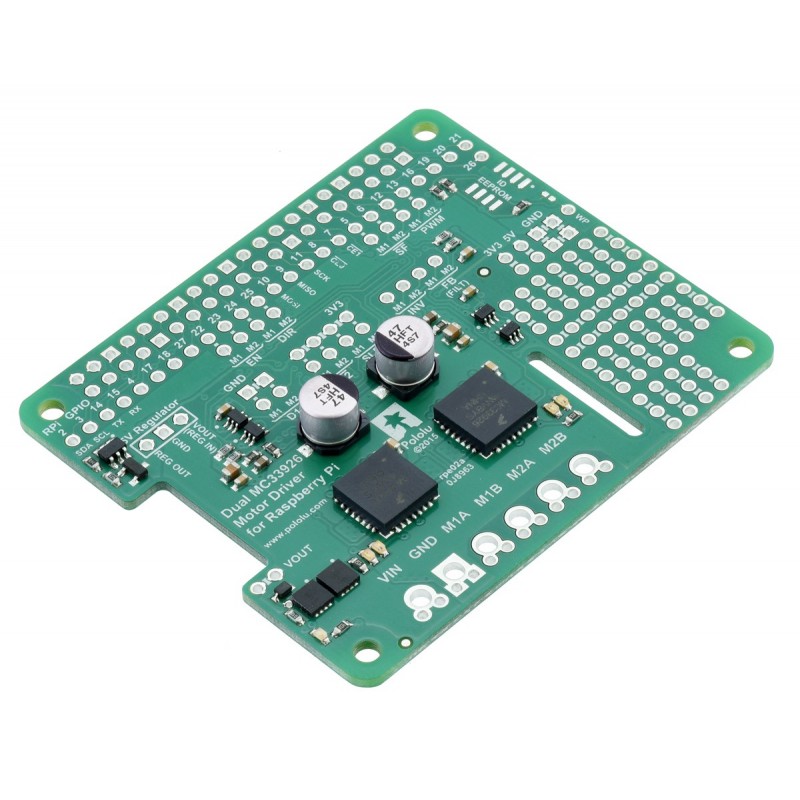
This add-on board enables a Raspberry Pi B+, Pi A+, Pi 2 or Pi 3 to drive a pair of brushed DC motors. Its dual MC33926 motor drivers operate from 5 V to 28 V and can deliver a continuous 3 A (5 A peak) per motor. The default pin mappings make it easy to get started using our provided software, but the board also exposes most of the driver chips’ I/O pins for more specialized applications.
The board’s default configuration uses six GPIO pins to control the motor drivers, making use of the Raspberry Pi’s hardware PWM outputs, and it uses two additional pins to read status outputs from the drivers. However, the pin mappings can be customized if the defaults are not convenient, and other control inputs and outputs of the MC33926 ICs are accessible on the board for more advanced applications.This motor driver board is an add-on for the Raspberry Pi Model B+, Model A+, Pi 2 Model B, or Pi 3 Model B that lets it easily control a pair of bidirectional, brushed DC motors. The expansion board uses a pair of Freescale MC33926 motor drivers, which operate from 5 to 28 V and can deliver a continuous 3 A per channel (up to 5 A per channel for a few seconds). Other features include a reverse battery protection circuit and logic gates that reduce the number of I/O pins required to control the driver ICs effectively. The board ships fully populated with its SMD components; it is available either as a partial kit, with a female header and terminal blocks included but not soldered in, or fully assembled with these connectors soldered to the PCB.
We also have a similar dual MC33926 shield for Arduinos and Arduino-compatible boards and basic single and dual MC33926 carriers for those using a different controller or with tighter space constraints. For a smaller, lower power, and lower cost alternative, consider the DRV8835 Dual Motor Driver for Raspberry Pi.Note that this motor driver add-on is designed specifically for newer versions of the Raspberry Pi with 40-pin GPIO headers, including the Model B+, Model A+, Raspberry Pi 2 Model B, and Raspberry Pi 3 Model B. The board matches the Raspberry Pi HAT (Hardware Attached on Top) mechanical specification, although it does not conform to the full HAT specifications due to the lack of an ID EEPROM. (A footprint for adding your own EEPROM is available for applications where one would be useful; pull-ups on SDA, SCL, and WP are provided.) It is not practical to use this expansion board with the original Raspberry Pi Model A or Model B due to differences in their pinout and form factor.
This version of the motor driver is a partial kit, with connectors included but not soldered in. (See item #2756 for an assembled version.)
Three 2-pin, 5 mm terminal blocks are included for making easy motor and power connections to the board once they have been slid together and soldered to the six large through-holes. Alternatively, you can solder 0.1″ male header pins to the smaller through-holes below the terminal block holes, or you can just solder wires directly to the board.The 2×20-pin 0.1″ female header should be mounted to the bottom of the board (the side opposite the surface-mount components). Once soldered, this header is used to connect the board to the Raspberry Pi’s 40-pin GPIO header. Alternatively, if you want to continue to have access to the Raspberry Pi’s 40 GPIO pins while the motor driver board is plugged in, you can install a stackable 2×20-pin female header (not included) instead.
Shorting blocks and 0.1″ male headers (not included) can be used to make some of the more advanced optional modifications to the board, such as remapping the control pins.The motor driver ships with a set of four M2.5 standoffs (11 mm length), screws, and nuts that can be used to secure the board to the Raspberry Pi at the proper height for the GPIO connector. If you decide not to use the standoffs, be careful not to allow the motor and power connections to short against the Raspberry Pi’s HDMI connector.
A Raspberry Pi is not included.
This section explains how to use the dual MC33926 motor driver add-on board and provides some basic information about the motor driver pins to help get you started. However, we strongly encourage you to consult the MC33926 datasheet (1MB pdf) for detailed pin descriptions, truth tables, and electrical characteristics. This expansion board is essentially a breakout board for two MC33926 motor driver ICs with additional logic circuitry to simplify the motor control, so the datasheet is your best resource for answering questions not covered here.
A reverse-voltage protection circuit helps prevent damage to the board in case the motor power supply is connected backward. The reverse-protected input voltage can be accessed for use in other circuits through the two pins labeled VOUT on the left side of the board.In the board’s default state, the motor driver outputs and the Raspberry Pi are powered separately, though they share a common ground and the board’s 3.3 V logic supply is provided by the Raspberry Pi. When used this way, the Raspberry Pi must be powered via its USB Micro-B receptacle, and the motor driver board must be supplied with 5 V to 28 V through its large VIN and GND pads. However, the motor driver board provides a set of three through-holes where you can conveniently connect an appropriate voltage regulator, allowing the motor supply to also power the Raspberry Pi (see the Powering the Raspberry Pi from the motor driver board section below).
The board includes logic gates that enable drive/brake operation of the MC33926 drivers with only two control pins per motor (PWM and direction). As drive/brake operation usually provides a more linear relationship between PWM duty cycle and motor speed than drive/coast operation, we generally recommend using drive/brake operation when possible.
This table shows how the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pins are used to interface with the motor drivers:
| RPi GPIO pin |
Motor driver pin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Motor 1 SF | Status flag output: When the driver is functioning normally, this pin should be pulled high by the Raspberry Pi. In the event of a driver fault , the driver IC drives SF low. If either of the disable pins (D1 or D2) is disabling the outputs, SF will also be low. |
| 6 | Motor 2 SF | |
| 12 | Motor 1 PWM | Motor speed input: A PWM (pulse-width modulation) signal on this pin corresponds to a PWM output on the corresponding driver’s motor outputs. When this pin is low, the motor brakes low. When it is high, the motor is on. The maximum allowed PWM frequency is 20 kHz. |
| 13 | Motor 2 PWM | |
| 22 | Motor 1 EN | Enable input: This pin is internally pulled low, putting the motor driver IC into a low-current sleep mode and disabling the motor outputs (setting them to high impedance). EN must be driven high to enable the motor driver. |
| 23 | Motor 2 EN | |
| 24 | Motor 1 DIR | Motor direction input: When DIR is low, motor current flows from output A to output B; when DIR is high, current flows from B to A. |
| 25 | Motor 2 DIR |
This table shows how the drivers’ control inputs affect the motor outputs:
| Inputs | Outputs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN | DIR | PWM | MxA | MxB | operating mode |
| 1 | 0 | PWM | PWM (H/L) | L | forward/brake at speed PWM % |
| 1 | 1 | PWM | L | PWM (H/L) | reverse/brake at speed PWM % |
| 1 | X | 0 | L | L | brake low (outputs shorted to ground) |
| 0 | X | X | Z | Z | coast (outputs off) |
All of the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pins are broken out along a row of numbered through-holes just below the 40-pin GPIO connector. Each GPIO pin used by the board is connected from this row to the corresponding motor driver pin by a trace on the underside of the board spanning the pair of holes. If you want to remap one of these motor driver pins, you can cut its trace with a knife and then run a wire from the lower hole to a new GPIO pin.
Using additional MC33926 pins:Note that the default pin mappings were chosen so that the Raspberry Pi’s default GPIO pull-ups and pull-downs match the direction the motor driver pins are or should be pulled (up for SF, down for others); if you remap the motor driver pins without paying attention to this, you might encounter issues with pins being pulled the wrong way. See the Raspberry Pi documentation for more about the default GPIO states.
The rest of the MC33926 inputs and outputs are not connected to the Raspberry Pi, but they are accessible through their own through-holes in case you want to use them in a more advanced application of the motor drivers. The board ties some of the inputs high or low through cuttable traces, similar to the way the remappable pins are connected, and you should cut the trace before connecting each input to anything else. This table shows the default configuration of the additional pins:
| Motor driver pin | Description | Default configuration on board |
|---|---|---|
| D1 | Disable input 1(active high) | Tied low (inactive) through cuttable trace |
| D2 | Disable input 2 (active low) | Tied high (inactive) through cuttable trace |
| SLEW | Slew rate selection | Tied high to select fast slew rate through cuttable trace |
| INV | Input invert | Internally pulled low (non-inverted) |
| FB | Feedback (current sense output) | Connected to sense resistor and low-pass filter to output approx. 360 mV/A |
On the left side of the expansion board is a set of three pins surrounded by a box labeled “5V Regulator”. The “VOUT (REG IN)” pin provides access to the driver board’s motor supply voltage after reverse-voltage protection, while the “REG OUT” pin is connected to the Raspberry Pi’s 5V power rail through an ideal diode circuit. If a suitable voltage regulator is connected to these three pins, it can generate 5 V to power the Raspberry Pi from the board’s motor supply voltage. We suggest using our D24V5F5 or D24V10F5 switching step-down regulators, which work at input voltages up to the 28 V maximum of the MC33926 and can supply up to 500 mA or 1 A of current, respectively, to the Raspberry Pi.
When adding a voltage regulator to the motor driver board, take care to orient it correctly: note that the motor driver board’s “VOUT (REG IN)” pin should connect to the regulator’s VIN pin, while the regulator’s VOUT pin should connect to the motor driver board’s “REG OUT” pin.
There are a few considerations to keep in mind when “back-powering” the Raspberry Pi through a voltage regulator in this way:
The ideal diode circuit makes it safe to have a different power supply connected to the Raspberry Pi through its USB Micro-B receptacle while the motor driver add-on and regulator are connected and powered.
Each MC33926 motor driver IC has a maximum continuous current rating of 5 A. However, the actual current it can deliver depends on how well you can keep it cool. The motor driver board is designed to draw heat out of the motor driver chips, but performance can be improved by adding heat sinks.
Unlike many other H-bridges, the MC33926 has a feature that allows it to gracefully reduce current as the current exceeds 5 A or as the chip temperature approaches its limit. This means that if you push the chip close to its limit, you will see less power to the motor, but it might allow you to avoid a complete shutdown.
We tested this motor driver board at room temperature with no forced air flow or heat sinks. In our tests, the board was able to deliver 5 A to both channels simultaneously for about 10 s before the thermal protection started reducing the current. The board delivered 4 A on both channels for about 40 s, and at 3 A it was able to operate continuously for over 10 minutes without triggering current limiting or thermal protection.
Our tests were conducted at 100% duty cycle; PWMing the motor will introduce additional heating proportional to the frequency.
This product can get hot enough to burn you long before the chip overheats. Take care when handling this product and other components connected to it.
| Size: | 65 mm × 56 mm |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 14 g1 |
| Motor driver: | MC33926 |
|---|---|
| Motor channels: | 2 |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 5 V2 |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 28 V3 |
| Continuous output current per channel: | 3 A |
| Peak output current per channel: | 5 A |
| Maximum PWM frequency: | 20 kHz |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | Y |
| Partial kit?: | Y |
Manufacturer BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Poland sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Responsible person BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Poland sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Raspberry Pi 3 model B (Quad Core Broadcom BCM2837, 4x1.2GHz ARM Cortex-A53, RAM 1GB, 4xUSB, Ethernet, HDMI, Wifi, Bluetooth)
No product available!
The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ is boasting a 64-bit quad core processor BCM2837B0 running at 1.4GHz, dual-band 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless LAN, Bluetooth 4.2/BLE, faster Ethernet, and PoE capability via a separate PoE HAT
Module with a 2-channel driver for DC motors TB6612FNG designed to work with the Raspberry Pi. It can work with voltages from 6 to 12 V and currents up to 3 A. SB Components 21468
The module with a 4-channel L293D DC motor driver, designed to work with the Raspberry Pi. It can work with a voltage from 6 to 24 V and a current of up to 600 mA. SB Components 08001
The official extension module (HAT) dedicated to the Raspberry Pi. It allows you to control LEGO SPIKE Prime motors and service LEGO sensors. Raspberry Pi SC0622
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of three drives using the I2C interface. Board with soldered connectors. Pololu 5033
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of three drives using the I2C interface. Connectors for self-assembly. Pololu 5034
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of three drives using the I2C interface. Pololu 5035
Extension module with a driver for two stepper motors based on the HR8825 system. Dedicated for Raspberry Pi minicomputers. Waveshare Stepper Motor HAT (B)
Extension module with a driver for two stepper motors based on the DRV8825 system. Dedicated for Raspberry Pi minicomputers. Waveshare Stepper Motor HAT
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board without connectors. Pololu 5059
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board with connectors for assembly. Pololu 5058
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board with soldered connectors. Pololu 5057
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board without connectors. Pololu 5056
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board with connectors for assembly. Pololu 5055
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board with soldered connectors. Pololu 5054
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board without connectors. Pololu 5053
No product available!
DC motor driver that allows you to control the movement of two drives using the I2C interface. Board with connectors for assembly. Pololu 5052
No product available!

This add-on board enables a Raspberry Pi B+, Pi A+, Pi 2 or Pi 3 to drive a pair of brushed DC motors. Its dual MC33926 motor drivers operate from 5 V to 28 V and can deliver a continuous 3 A (5 A peak) per motor. The default pin mappings make it easy to get started using our provided software, but the board also exposes most of the driver chips’ I/O pins for more specialized applications.
