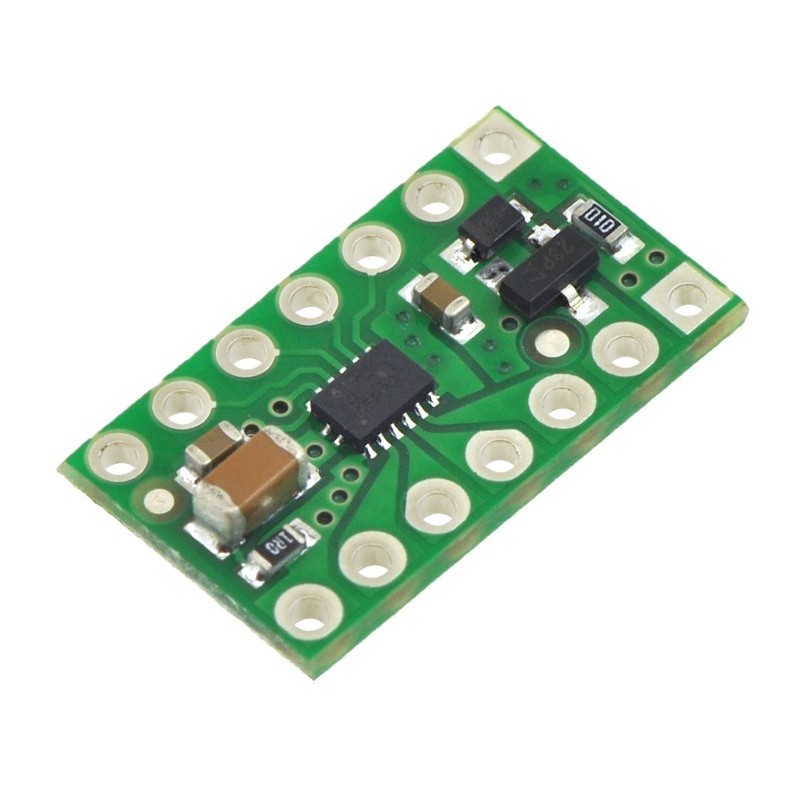


This tiny breakout board for TI’s DRV8835 dual motor driver can deliver 1.2 A per channel continuously (1.5 A peak) to a pair of DC motors, and it supports two possible control interfaces for added flexibility of use: IN/IN and PHASE/ENABLE. With an operating voltage range from 2 to 11 V and built-in protection against reverse-voltage, under-voltage, over-current, and over-temperature, this driver is a great solution for powering up to two small, low-voltage motors. The carrier board has the form factor of a 14-pin DIP package, which makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards and 0.1” perfboards.
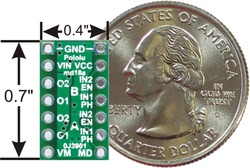 |
| DRV8835 dual motor driver carrier, bottom view with dimensions. |
|---|
 |
| TI SN754410 (16-pin DIP) next to the DRV8835 dual motor driver carrier (14-pin DIP) for size reference. |
|---|
Texas Instruments’ DRV8835 is a tiny dual H-bridge motor driver IC that can be used for bidirectional control of two brushed DC motors at 2 to 11 V. It can supply up to about 1.2 A per channel continuously and can tolerate peak currents up to 1.5 A per channel for a few seconds, making it an ideal driver for small motors that run on relatively low voltages. The DRV8835 is a great IC, but its small, leadless package makes it difficult for the typical student or hobbyist to use; our breakout board gives this driver the form factor of a 14-pin DIP package, which makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards and 0.1” perfboards. Since this board is a carrier for the DRV8835, we recommend careful reading of the DRV8835 datasheet. The board ships populated with SMD components, including the DRV8835, and adds a FET for reverse battery protection.
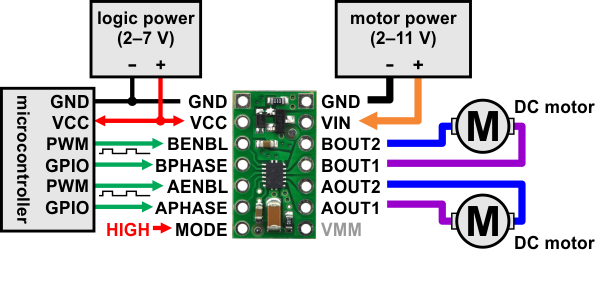 |
| Minimal wiring diagram for connecting a microcontroller to a DRV8835 dual motor driver carrier in phase-enable mode. |
|---|
Motor and motor power connections are made on one side of the board and logic power and control connections are made on the other. Each control input is pulled low through a weak pull-down resistor (approximately 100 kΩ), so the driver will be in the IN/IN mode if the MODE pin is left disconnected, and the driver outputs will be disabled by default. The driver requires a motor voltage between 2 and 11 V and a logic voltage between 2 and 7 V; the logic voltage can typically be supplied by or shared with the controlling device.
The DRV8835 features two possible control modes: IN/IN and PHASE/ENABLE. The MODE pin determines the control interface. Setting the MODE pin high, either with a pull-up resistor or a driving-high I/O line, sets the driver to PHASE/ENABLE mode, where the PHASE pin determines the motor direction and the ENABLE pin can be supplied with a PWM signal to control the motor speed. This mode is generally easier to use as it only requires one PWM per channel, but it only allows for drive/brake operation. (Drive/brake operation usually provides a more linear relationship between PWM duty cycle and motor speed than drive/coast operation, and we generally recommend using drive/brake operation when possible.)
| Simplified drive/brake operation with MODE=1 (PHASE/ENABLE) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| xPHASE | xENABLE | xOUT1 | xOUT2 | operating mode |
| 1 | PWM | L | PWM | reverse/brake at speed PWM % |
| 0 | PWM | PWM | L | forward/brake at speed PWM % |
| X | 0 | L | L | brake low (outputs shorted to ground) |
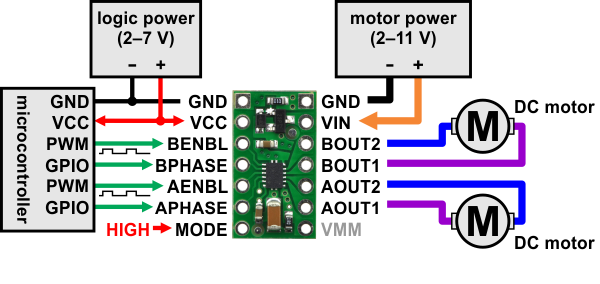 |
| Minimal wiring diagram for connecting a microcontroller to a DRV8835 dual motor driver carrier in in-in mode. |
|---|
When the MODE pin is disconnected or low, the control interface is IN/IN, which allows for slightly more advanced control options. The following truth table show how to achieve drive/coast and drive/brake operation using the IN/IN control interface:
| Drive/coast or drive/brake operation with MODE=0 (IN/IN) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| xIN1 | xIN2 | xOUT1 | xOUT2 | operating mode |
| 0 | 0 | OPEN | OPEN | coast (outputs off) |
| 0 | PWM | L | PWM | reverse/coast at speed PWM % |
| PWM | 0 | PWM | L | forward/coast at speed PWM % |
| PWM | 1 | L | PWM | reverse/brake at speed 100% − PWM % |
| 1 | PWM | PWM | L | forward/brake at speed 100% − PWM % |
| 1 | 1 | L | L | brake low (outputs shorted to ground) |
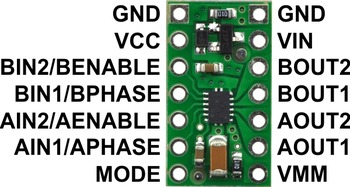 |
| PIN | Default State | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | 2–11 V motor power supply connection. Operation at low VIN voltages slightly reduces the maximum current output. | |
| VCC | 2–7 V logic power supply connection. This should be at or near the logic voltage of the control signal source. | |
| VMM | This pin gives access to the motor power supply after the reverse-voltage protection MOSFET (see the board schematic below). It can be used to supply reverse-protected power to other components in the system. It is generally intended as an output, but it can also be used to supply board power. | |
| GND | Ground connection points for the motor and logic power supplies. The control source and the motor driver must share a common ground. | |
| AOUT1 | The motor A half-bridge 1 output. | |
| AOUT2 | The motor A half-bridge 2 output. | |
| BOUT1 | The motor B half-bridge 1 output. | |
| BOUT2 | The motor B half-bridge 2 output. | |
| AIN1/APHASE | LOW | A logic input control for motor channel A. |
| AIN2/AENABLE | LOW | A logic input control for motor channel A. |
| BIN1/BPHASE | LOW | A logic input control for motor channel B. |
| BIN2/BENABLE | LOW | A logic input control for motor channel B. |
| MODE | LOW | Logic input that determines the control interface. Logic low on this pin results in IN/IN mode while logic high results in PHASE/ENABLE mode. |
The DRV8835 datasheet recommends a maximum continuous current of 1.5 A per motor channel. However, the chip by itself will overheat at lower currents. For example, in our tests at room temperature with no forced air flow, the chip was able to deliver 1.5 A per channel for approximately 15 seconds before the chip’s thermal protection kicked in and disabled the motor outputs, while a continuous current of 1.2 A per channel was sustainable for many minutes without triggering a thermal shutdown. The actual current you can deliver will depend on how well you can keep the motor driver cool. The carrier’s printed circuit board is designed to draw heat out of the motor driver chip, but performance can be improved by adding a heat sink. Our tests were conducted at 100% duty cycle; PWMing the motor will introduce additional heating proportional to the frequency.
This product can get hot enough to burn you long before the chip overheats. Take care when handling this product and other components connected to it.
|
|
Two 1×7-pin breakaway 0.1” male headers are included with the DRV8835 dual motor driver carrier, which can be soldered in to use the driver with perfboards, breadboards, or 0.1” female connectors. (The headers might ship as a single 1×14 piece that can be broken in half.) The right picture above shows the two possible board orientations when used with these header pins (parts visible or silkscreen visible). You can also solder your motor leads and other connections directly to the board.
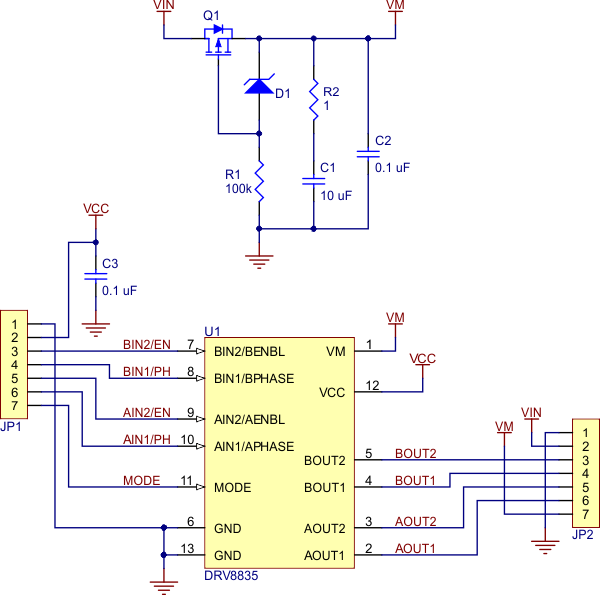 |
| Schematic of the DRV8835 dual motor driver carrier. |
|---|
Download:
Data sheet
Manufacturer BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Poland sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
Responsible person BTC Korporacja sp. z o. o. Lwowska 5 05-120 Legionowo Poland sprzedaz@kamami.pl 22 767 36 20
TB6612FNG Dual Motor Driver Carrier
Miniature medium-power, 6 V brushed DC motor with a 51.45:1 metal gearbox. It has a cross section of 10 × 12 mm, and the D-shaped gearbox output shaft is 9 mm long and 3 mm in diameter. Pololu 2365
No product available!
10:1 Micro Metal Gearmotor MP
No product available!
298:1 Micro Metal Gearmotor MP
This add-on board makes it easy to control two high-power DC motors with a Raspberry Pi. Its twin discrete MOSFET H-bridges support a wide 6.5 V to 36 Voperating range and are efficient enough to deliver a continuous 14 A without a heat sink. The drivers offer basic current limiting functionality, and they accept ultrasonic PWM frequencies for quieter operation.
Pololu High-Power Motor Driver 36v20 CS
Pololu High-Power Motor Driver 36v15
Pololu High-Power Motor Driver 36v9
Pololu Jrk 21v3 USB Motor Controller with Feedback
No product available!
Pololu Jrk 21v3 USB Motor Controller with Feedback (Fully Assembled)
No product available!
Dual-channel electric motors controller (H-bridge) Arduino Motor Shield Rev3 with L298 for controlling two DC motors or one stepper motor with the possibility of using an electronic brake.
No product available!
DRV8835 Dual Motor Driver Carrier
The board based on the L298 Dual Full-Bridge Motor Driver; can provide up to 4 Amps of current to the motors (2 Amps per motor). ROB-09571
No product available!
Motor-driven expansion board for Arduino, L293D, 74HC595 shift register, RoHS
Dual H-Bridge motor driver board, 2A, 36V max, L298N, RoHS
(DRI0009) 2A Motor Shield For Arduino
DRV8801 Single Brushed DC Motor Driver Carrier
A4990 Dual Motor Driver Carrier
This Kit with fully-dedicated PWM driver chip handles all the motor and speed controls over I2C. Only two data pins (SDA & SCL in addition to the power pins GND & 5V) are required to drive the multiple motors; you can also connect any other I2C devices or shields to the same pins. This makes it drop-in compatible with any Arduino, such as the Uno, Due, Leonardo and Mega R3. Adafruit 1438
This shield makes it easy to control two high-power DC motors with your Arduino or Arduino-compatible board. Its dual robust VNH5019 motor drivers operate from 5.5 to 24 V and can deliver a continuous 12 A (30 A peak) per motor, or a continuous 24 A (60 A peak) to a single motor connected to both channels. Pololu 2507
No product available!

DRV8835 Dual Motor Driver Carrier
